
The price of protection: Why cyber insurance premiums are on the rise
Cyber insurance premiums are on the rise and policies are offering lower coverage. Learn how you can secure and protect your business.…




Oliver Pinson-Roxburgh
CEO and Co-Founder
09th October 2023
With the rise of technological advances, businesses often lean towards prioritising functionality and meeting customer needs when launching new products or updates. With security often being an afterthought or no thought at all. This approach can result in the presence of vulnerabilities within the product and, in some cases, throughout the entire supply chain.
Businesses can overcome this challenge by shifting towards a secure by design approach, integrating security measures from the outset. This concept incorporates product, software development, and other functions such as procurement.
In this blog, we’ll explore the significance of a secure by design and default mindset, its importance, and practical applications.
Secure by design is a cybersecurity and software development approach that integrates security measures and considerations at every stage of the design and development process. Rather than attempting to add security as an afterthought or patch, this methodology aims to create systems, applications or products that are inherently designed to be secure.
This strategy can reduce the risk of security breaches and organizations can lessen the likelihood of expensive data breaches, legal repercussions, and reputational harm by incorporating a shared responsibility to security from the start.
As an example, imagine an e-commerce site that adopts a secure by design mindset. By using encryption, secure authentication, and strict access controls, the development team can ensure that user data, such as personal information and payment information, is protected throughout a customer’s purchase journey. As a result it would be very difficult for attackers to compromise sensitive customer information, or find vulnerabilities in the website to exploit.
This proactive approach not only protects customer data but also shields the company from the negative financial and reputational effects of a data breach, which ultimately fosters greater customer loyalty and trust.
A crucial but frequently disregarded aspect of ensuring the security and integrity of digital systems is the idea of ‘security by default’. This is one component of ‘security by design’ and describes the pre-configured options and parameters included with software, operating systems, and hardware right out of the box. These options are created to strike a balance between practicality and security, making the product usable and accessible for the typical user. However, they can have a profound influence on user behaviour and system security.
Default security settings play an important role in shaping user behaviour because most people tend to stick with the settings that are already in place. Users frequently rely on the default settings because they are unaware of or unmotivated to configure the settings themselves. This can lead to users implementing weak security measures and putting their data at unnecessary risk.
The effectiveness of default security settings lies in their capacity to influence user behaviour and establish the minimum level of security for digital systems. Setting strong, user-friendly defaults is essential for developers and manufacturers to guarantee the security and privacy of their users while also promoting best practices in cybersecurity.
An example of security by default is password complexity rules. Many websites and applications enforce password complexity rules by default. When a user creates an account or changes their password, the system may require the password meets certain criteria such as:
By enforcing these password complexity rules by default, the system ensures that users create stronger and more secure passwords without giving them an alternative. This reduces the likelihood of weak or previously compromised passwords being used and strengthens the overall security of the system.
Here are just a few of the ways that businesses can benefit from adopting a robust secure by design and default strategy:
Ultimately, embracing secure by design and secure by default methodologies can lead to better products and better experiences for users. This approach can also help businesses avoid paying large sums of money to fix security flaws and the need for additional compensating controls.
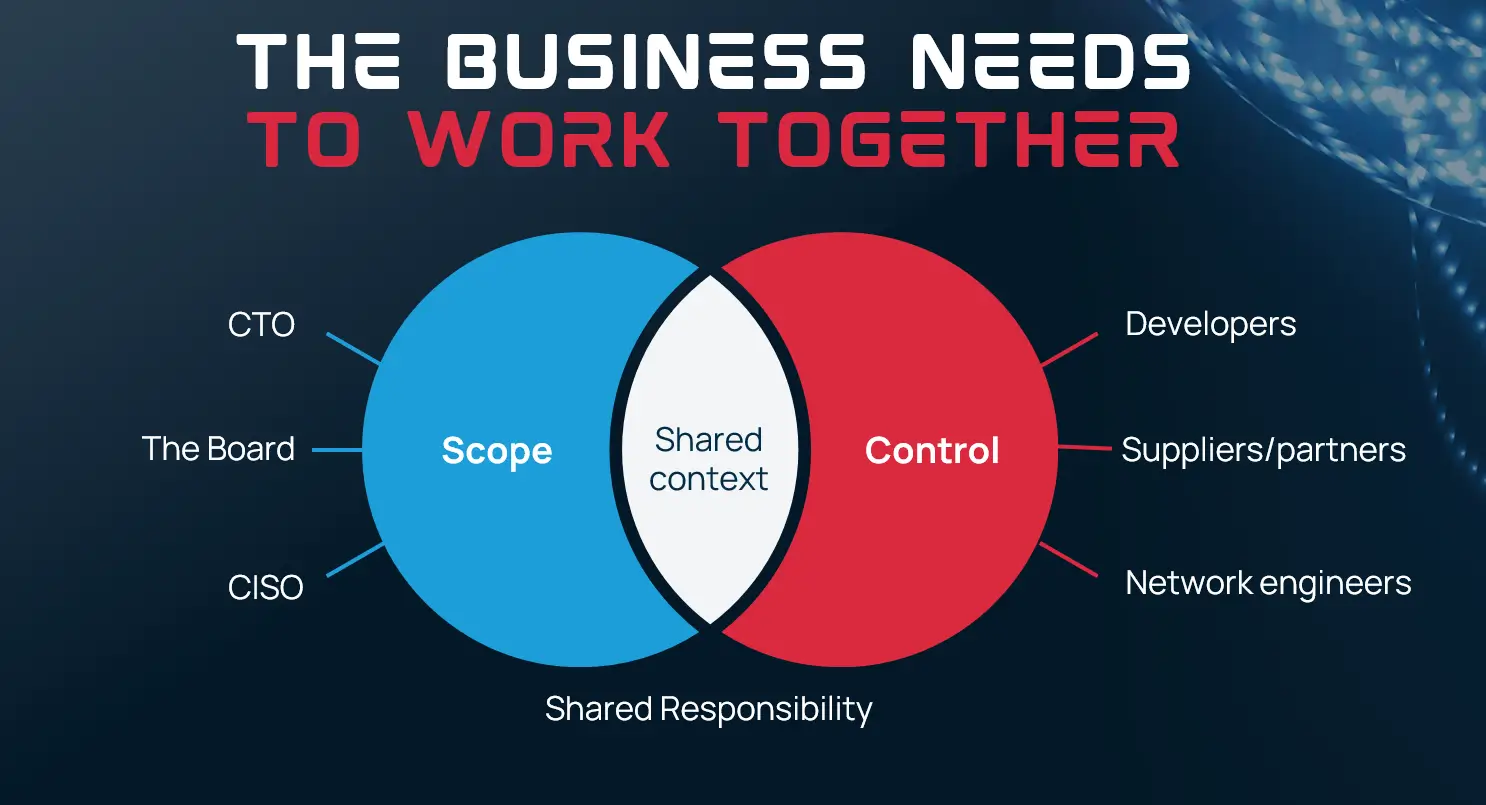
It’s important to realise that secure by design is a concept that applies to all areas of a product lifecycle and different areas of a business. Although developers are essential to the creation of secure software, secure design principles go beyond coding. The reality is that all stakeholders that work on a product should be responsible for maintaining a secure by design mindset, from board members to developers, partners and third-party suppliers.
Developers undoubtedly have a significant influence over the security of a software or application. They are responsible for writing code, implementing encryption, and ensuring data protection. However, their scope and control are often limited to the technical aspects of the project. To create a robust and resilient security infrastructure, it is imperative that all stakeholders recognise their role in the process.
The CTO is crucial in promoting the secure by design methodology. They are in charge of establishing the organization’s technological vision and strategy. The CTO ensures that security is woven into the fabric of every project by highlighting security as a fundamental principle from the beginning, avoiding the need for expensive modifications in the future.
The CISO acts as the guardian of security within the company. Their expertise is invaluable in defining security policies, conducting risk assessments, and guiding the implementation of security measures. CISOs play a central role in ensuring that security isn’t an isolated concern but an integral part of the business strategy.
Equally critical is the involvement of the board members. They hold the ultimate responsibility for the company’s success, and that includes safeguarding its assets and reputation. Board members need to understand the implications of security vulnerabilities and allocate the necessary resources to protect the organization.
Developers, while essential to the secure by design process, do indeed have limitations in terms of their scope and control. However their role in writing secure code and following best practices is pivotal. They need to collaborate closely with CISOs and network engineers to understand the latest threats and vulnerabilities and implement appropriate safeguards.
Suppliers and partners, often overlooked in the security conversation, must also share some responsibility. Any security vulnerabilities in their products or services can pose significant risks to the entire ecosystem. Collaboration with suppliers and partners ensures that security is upheld throughout the supply chain.
Lastly, network engineers are responsible for the infrastructure that supports software and systems. They need to work hand in hand with developers to ensure that network configurations are secure and resilient against cyber threats.
To successfully implement a secure by design approach, security considerations must be included from the beginning of the development process. This can include the development of threat models, identifying potential vulnerabilities, and adhering to industry standards. It’s also important to evaluate your security measures and prioritise regular security testing to identify and defend against new and evolving threats.
Here are my five recommendations to help you implement a robust security by design strategy within your business:
Vendor assessment: Establish a rigorous process for evaluating the security posture of third party software vendors before making any purchasing decisions. This includes assessing their track record, security certifications, and any past security incidents. If you rely on their product or service for yours to function, then you should uphold that vendor to the same standards that you do internally.
Security requirements: Clearly define security requirements and standards that software must meet. This ensures that security is a top priority during the procurement process.
Regular reviews: Continuously review and update your procurement policies to adapt to evolving security threats and industry best practices.
Access control: Implement robust access control measures to ensure that only authorised personnel have access to sensitive systems and data.
Security Operations Centre (SOC): Establish a SOC to monitor your IT environment for security incidents and respond promptly to any breaches or anomalies. You could outsource this function to save yourself the resource and cost overhead, while still achieving 24/7 coverage.
Incident response place: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines how your organization will react to and recover from security incidents.
Vendor collaboration: Establish strong relationships with key IT suppliers. Engage in ongoing communication to address security concerns, share threat intelligence, and collaborate on security improvements.
Third party risk management: Implement a robust third-party risk management programme to continuously assess and mitigate security risks associated with your suppliers.
Information sharing: Actively participate in industry forums, associations, and information sharing networks to stay informed about emerging security threats and best practices.
Peer reviews: Collaborate with industry peers to exchange insights and conduct peer reviews of software, products, and services to identify those that align best with secure by design principles.
Benchmarking: Use industry benchmarks and standards as a reference to assess the security maturity of your organization and compare it with others.
Shared responsibility agreement: Clearly define the responsibilities of both your organization and your technology supplier in a shared responsibility model. Understand what security aspects are managed by each party.
Regular communication: Maintain open lines of communication with your technology supplier to address security concerns, updates, and changes in responsibilities.
Compliance and auditing: Regularly audit and assess the security measures in place, both internally and with third party suppliers, to ensure compliance with the shared responsibility model.
Once the necessary steps have been taken to develop or purchase your new software or tool, there must be an ongoing commitment to ensuring the security and integrity of the product is upheld.
Here are a few best practices that I would recommend:
Conduct thorough vulnerability scans on a regular basis to find and fix any potential flaws or vulnerabilities in your tool or software.
To strengthen the security posture of your software, take effective hardening measures. This includes setting up your system and application to adhere to industry best practices and reduce attack surfaces. For example applying regular software updates.
Safeguarding sensitive data is paramount. Enforce strict data privacy controls, adhering to regulatory standards and best practices to secure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of critical data.
Conduct regular penetration tests to simulate real-world attacks and assess the resilience of your software or tool. By identifying vulnerabilities from an attacker’s perspective, you can strengthen your defences before a threat actor exploits them.
For the early detection of security incidents or anomalies, ongoing monitoring is crucial. Utilise cutting-edge monitoring techniques and tools to keep a close eye on the performance and security of your software, enabling quick reaction to any potential threats.
By carefully following these best practices, you can strengthen the security of your software or product, ensuring that it continues to be a robust and resilient asset within your business operations.
In an increasingly interconnected and vulnerable digital world, it’s about protecting not only your company, but also your customers and partners. By prioritising security from the start and committing to it on an ongoing basis, you can ensure that your products and services are not only functional and appealing but also resilient in the face of the rapidly changing cyber threats. Security by design is not an option; it’s a shared responsibility.

Oliver Pinson-Roxburgh
CEO and Co-Founder
Share this article
Get in touch today to start your free trial of Defense.com™ and discover how we can help you take the stress out of your cybersecurity.

Cyber insurance premiums are on the rise and policies are offering lower coverage. Learn how you can secure and protect your business.…

Understand how to conduct a step-by-step cybersecurity risk assessment to help you identify, assess and manage cyber risks that could affect your business.…

Learn about the security risks involved with cloud computing, how to secure your data, and risk management best practices.…

How well prepared is your business to withstand and recover from a cyber attack? Discover best practice advice on how to best prepare.…
Get actionable cyber security advice and insights straight to your inbox.